Haptic Feedback in Surgical Robotics: Restoring the Surgeon's Touch
In the realm of modern medicine, minimally invasive surgical procedures have revolutionized the way we approach various medical interventions. Robotic-assisted surgery, in particular, has become increasingly prevalent, offering numerous benefits such as enhanced precision, improved dexterity, and reduced patient trauma. However, one critical aspect that has been lacking in many robotic surgical systems is the ability to convey accurate haptic feedback, or the sense of touch, to the surgeon operating the robotic instruments.
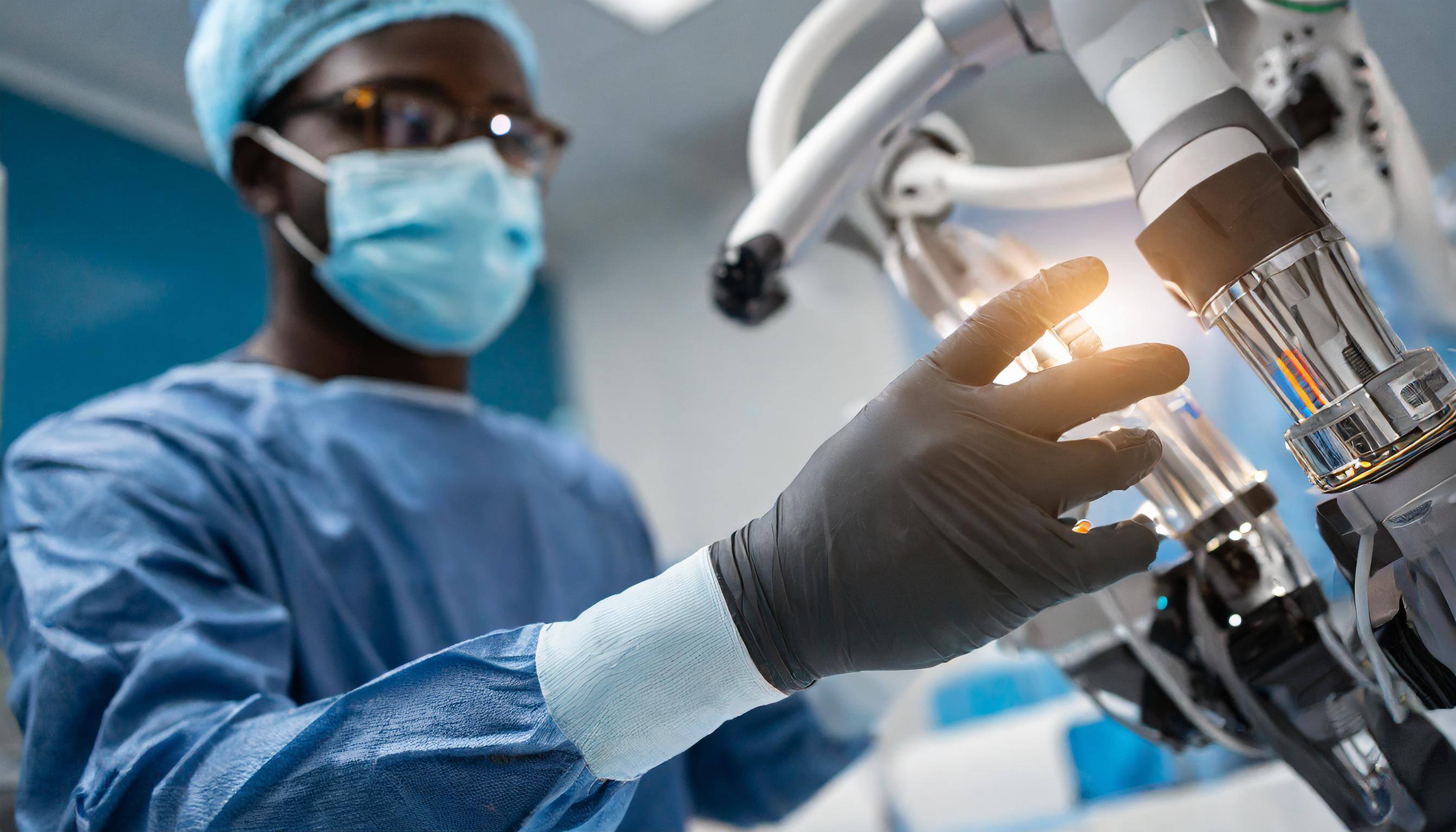
The importance of haptic feedback in surgery cannot be .jpg?width=300&height=171&name=Firefly%20A%20robotic%20surgical%20arm%20with%20force-sensing%20instruments%20interacting%20with%20simulated%20tissue.%20The%20(1).jpg) overstated. During traditional open surgical procedures, surgeons rely heavily on their sense of touch to assess tissue properties, detect anatomical structures, and gauge the appropriate amount of force to apply. This tactile information is crucial for making informed decisions and performing delicate maneuvers with precision and safety. In robotic surgery, however, the surgeon is physically separated from the patient, creating a disconnect between the surgeon's hands and the surgical site.
overstated. During traditional open surgical procedures, surgeons rely heavily on their sense of touch to assess tissue properties, detect anatomical structures, and gauge the appropriate amount of force to apply. This tactile information is crucial for making informed decisions and performing delicate maneuvers with precision and safety. In robotic surgery, however, the surgeon is physically separated from the patient, creating a disconnect between the surgeon's hands and the surgical site.
Researchers and engineers have recognized the significance of this challenge and have been actively exploring solutions to integrate haptic feedback into surgical robotics. By incorporating advanced sensor technologies and sophisticated control systems, it is now possible to detect and transmit tactile information from the surgical instruments to the surgeon's control interface, effectively restoring the sense of touch in a robotic environment.
 One promising approach involves the use of force-sensing instruments that can measure the interaction forces between the surgical tools and the patient's tissue. This data is then translated into tactile feedback, which can be conveyed to the surgeon through various methods, such as haptic interfaces or force-reflecting control systems. These interfaces allow the surgeon to feel the resistance, texture, and compliance of the tissues being manipulated, providing valuable sensory feedback that can enhance precision and safety during delicate procedures.
One promising approach involves the use of force-sensing instruments that can measure the interaction forces between the surgical tools and the patient's tissue. This data is then translated into tactile feedback, which can be conveyed to the surgeon through various methods, such as haptic interfaces or force-reflecting control systems. These interfaces allow the surgeon to feel the resistance, texture, and compliance of the tissues being manipulated, providing valuable sensory feedback that can enhance precision and safety during delicate procedures.
Another avenue of research focuses on incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to interpret and augment haptic feedback. By analyzing vast datasets of tactile information from previous surgical cases, AI algorithms can learn to recognize patterns and provide valuable insights to the surgeon. This could include highlighting potential areas of concern, suggesting appropriate force levels, or even guiding the surgeon through complex surgical maneuvers based on the tactile feedback received.
The integration of haptic feedback in surgical robotics holds immense potential for improving patient outcomes and reducing surgical complications. By restoring the sense of touch, surgeons can regain a critical sensory modality that has been largely absent in robotic procedures. This advancement not only enhances surgical  precision and safety but also opens up new possibilities for training and skill development, as novice surgeons can benefit from the tactile guidance provided by these advanced systems.
precision and safety but also opens up new possibilities for training and skill development, as novice surgeons can benefit from the tactile guidance provided by these advanced systems.
It is important to note that the successful implementation of haptic feedback in surgical robotics requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving expertise from various fields such as robotics, mechatronics, biomedical engineering, and human-computer interaction. Companies like Boston Engineering, with their expertise in embedded systems, sensors, industrial design, and product redesign, play a crucial role in addressing the challenges associated with haptic feedback and developing innovative solutions to mitigate these issues.
As we continue to push the boundaries of minimally invasive surgery, the integration of haptic feedback in surgical robotics stands as a critical frontier, promising to enhance precision, safety, and overall surgical outcomes. By restoring the sense of touch, we can empower surgeons with a more complete sensory experience, ultimately advancing the field of robotic-assisted surgery and improving patient care.
For almost three decades, Boston Engineering has designed, developed, and optimized devices and technologies the medical community relies on to save lives, enrich quality of life, and reduce costs to the healthcare system. We provide solutions to the challenges in the adoption of surgical robotics.
Our expertise includes industrial design and product redesign, sensors and control systems, robotics technical innovation, and digital software solutions.
Imagine your Impact: Stay up-to-date with the latest insights and trends we're watching. Add your email address below and sign up for a monthly summary of our most impactful posts!