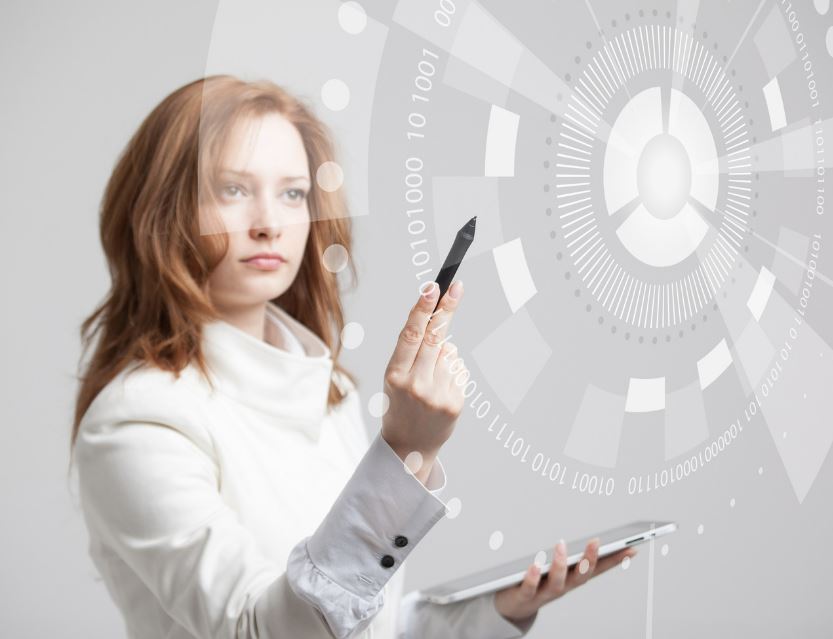
8 Key Engineering Elements in Product Commercialization
Discipline during the engineering phase of product commercialization allows companies to stay at the forefront of innovation, create differentiated offerings, and meet customer needs effectively.
Commercialization is a range of activities and specialized decisions that guide businesses in successfully bringing their innovative ideas, products, or technologies to market. Embracing these technology elements and strategies as an integral part of the commercialization process enhances the chances of developing successful products and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
What is the Product Commercialization Process?
Product commercialization refers to the process of introducing a new product or service into the market and making it available for sale to consumers. It involves all the activities and strategies that transform an idea, concept, or prototype into a marketable product. Commercialization is a crucial step in the product development cycle and involves various stages, including market research, product design and development, manufacturing, marketing, and sales.
Five key steps in the commercialization process:
- Marketing
- Technology
- Engineering
- Capitalizing
- Producing
Read more about Product Commercialization

The Key Elements of the Engineering Phase of Product Commercialization
- Scouting for Product Development: Scouting for Product Development involves the identification and evaluation of potential product ideas, either internally generated or sourced externally. This element focuses on gathering insights, market research, and exploring innovative concepts that align with business objectives. Scouting for new product ideas ensures a robust pipeline for development and enhances the chances of creating successful commercial offerings.
- Applied Research & Development: Applied Research & Development involves the systematic exploration of scientific principles and technologies to develop practical solutions for specific commercial applications. This element focuses on bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical implementation. Through applied research, businesses can validate technological feasibility, optimize performance, and mitigate risks associated with the product development process.
- Conceptual Design: Conceptual Design refers to the initial stage of product development, where ideas and requirements are translated into conceptual models or prototypes. This element involves brainstorming, sketching, and creating visual representations of the product's form, functionality, and features. Conceptual design helps stakeholders visualize the product, gather feedback, and make informed decisions before progressing to detailed design and development.
- Feasibility Studies: Feasibility Studies assess the technical, economic, and operational viability of a product concept. This element involves conducting analyses, evaluating market demand, assessing manufacturing capabilities, and estimating costs and potential returns on investment. Feasibility studies provide critical insights into the project's viability, helping businesses make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, development timelines, and overall project feasibility.
- Reverse Engineering: Reverse Engineering involves analyzing an existing product or system to understand its design, functionality, and components. This element is particularly useful when seeking to improve or replicate an already successful product. Reverse engineering enables businesses to gain insights into competitors' offerings, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the product's performance and features.
- Product Development: Product Development is the core process of transforming a product concept into a fully functional and marketable offering. This element involves detailed design, engineering, and prototyping, considering factors such as materials, manufacturing processes, and regulatory compliance. Product development requires close collaboration between engineers, designers, and other stakeholders to ensure the product meets customer needs, quality standards, and business objectives.
- Design for X: Design for X (where X can be manufacturing, assembly, cost, reliability, etc.) is an approach that focuses on optimizing the design of a product to achieve specific objectives. This element emphasizes factors such as manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, ease of assembly, reliability, and sustainability. Design for X* principles help minimize production costs, improve product performance, enhance user experience, and streamline the manufacturing process.
- Test and Validation: Test and Validation involve rigorous testing of the developed product to ensure its functionality, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. This element includes various testing methods, such as performance testing, stress testing, usability testing, and regulatory compliance testing. Through comprehensive testing and validation, businesses can identify and rectify any design flaws, refine the product's features, and ensure a high-quality end product.

Understanding the importance of the Product Commercialization Process

Ready to Begin your Product Commercialization Project?
 Whether you’ve created a new technology, or have an innovative way to use an existing solution, Boston Engineering will turn your ideas into reality. Our Commercialization experts and Industry Partners will enhance your current team or manage the entire Product Commercialization Process from Market Analysis to Production. Don't leave complex projects or high visibility product launches to chance. Know you're going to get the results you want by working with industry leaders in design, development, and deployment of innovative products driven by Novel Engineering. Contact Boston Engineering Today to get started.
Whether you’ve created a new technology, or have an innovative way to use an existing solution, Boston Engineering will turn your ideas into reality. Our Commercialization experts and Industry Partners will enhance your current team or manage the entire Product Commercialization Process from Market Analysis to Production. Don't leave complex projects or high visibility product launches to chance. Know you're going to get the results you want by working with industry leaders in design, development, and deployment of innovative products driven by Novel Engineering. Contact Boston Engineering Today to get started.
Let's start the Product Commercialization Conversation
No matter the challenge, our team possesses the expertise in the engineering disciplines and technologies you need to bring your vision to life. Impossible Challenge? Try Us.
Imagine your Impact: Stay up-to date- with the latest insights and trends we're watching. Add your email address below and sign up for a Monthly Summary of our most impactful posts!